Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating
Hydronic Radiant floor heating is increasingly popular among homeowners who want to enhance their home's comfort and energy efficiency. It's no surprise—this heating solution offers an even distribution of warmth that traditional methods like baseboard heaters or forced air systems can't match. The system provides a consistent and comfortable heat source, making it an appealing choice for many.
However, before you choose this system, there are important considerations to keep in mind, such as flooring compatibility, installation requirements, and warranties. In this article, we'll explore the benefits of hydronic radiant floor heating, discuss compatible flooring options, examine flooring types that should be avoided, and highlight installation and warranty considerations to ensure a successful result.
What is Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating?
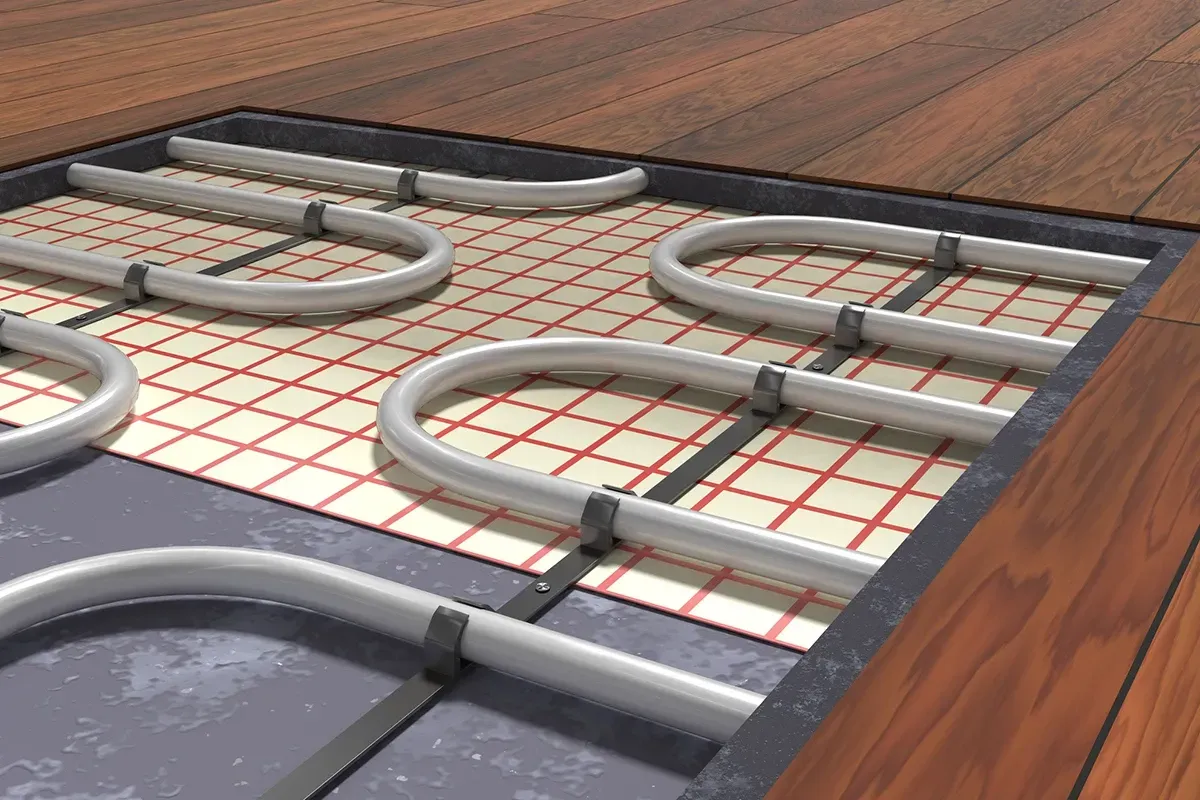
Hydronic radiant floor heating is a system that circulates warm water through a network of tubing installed beneath the floor to heat a space. Instead of heating the air as traditional systems do, hydronic floor heating works by directly warming the floor, which then radiates heat upward into the room. This method provides a comfortable, even distribution of heat that eliminates cold spots and drafts.
There are several reasons why hydronic radiant floor heating has gained popularity:
- Energy Efficiency: Hydronic systems operate at lower temperatures compared to forced air systems. By running at a consistent, lower temperature, they reduce the amount of energy needed to maintain warmth in your home.
- Even Heat Distribution: The heat spreads evenly across the floor, which naturally rises and fills the room. Unlike baseboard heaters that tend to concentrate heat in specific areas, radiant floor heating creates consistent warmth throughout.
- Comfort: The radiant heat from the floor feels naturally comfortable. Since it rises gradually, it heats the room from the ground up, which makes it less likely for the air to become dry, unlike forced air systems that can dry out the air in your home.
- No Noisy Fans or Ductwork: This type of heating operates quietly, unlike forced air heating systems that can be noisy as they push air through ducts.
Why Choose Hydronic Over Other Heating Systems?
Hydronic radiant floor heating has its unique advantages, but it also has to be compared to other types of heating solutions. If you're contemplating whether hydronic is the right choice for your home, it's useful to understand how it compares to traditional systems:
- Energy Savings: Hydronic systems tend to be more energy-efficient than traditional forced air systems. In a forced air system, heated air is distributed through ducts, which can lose heat if the ducts are not properly insulated. In contrast, a hydronic system directly heats the floor, reducing energy loss and increasing efficiency.
- No Allergens in the Air: Unlike forced air systems, hydronic systems do not circulate dust and allergens, which is beneficial for individuals with respiratory issues or allergies.
- Better Control Over Heating Zones: Hydronic systems allow for the creation of different heating zones in your home, which can be controlled independently. This means you can heat specific rooms or areas without wasting energy heating spaces that are not in use.
Flooring Types Compatible with Hydronic Systems
When considering hydronic radiant floor heating, choosing the right flooring is crucial for optimal performance. Some flooring materials are better suited for radiant heating systems because they allow heat to transfer efficiently, while others may act as insulators, reducing the effectiveness of the system. Below are some flooring options that are compatible with hydronic radiant floor heating:
- Tile and Stone: Ceramic tile, porcelain tile, and natural stone such as marble, slate, and granite are excellent conductors of heat. These materials allow the warmth from the hydronic system to transfer efficiently from the floor to the room. They are also durable and can withstand the temperature changes associated with radiant heating systems. If you choose tile or stone, make sure the adhesive and grout are also compatible with radiant heating to prevent damage over time.
- Luxury Vinyl Plank (LVP): LVP is a popular flooring option due to its durability and aesthetic variety. It is also a relatively good conductor of heat, making it compatible with hydronic radiant heating systems. However, not all LVP products are designed for use with radiant heating. Always check with the manufacturer to confirm compatibility before installation.
- Engineered Hardwood: Some engineered hardwood floors are designed to be used with radiant heating systems. Engineered hardwood is made from layers of wood, making it less prone to warping and expanding than solid hardwood. When selecting engineered hardwood, choose products that are explicitly labeled as compatible with radiant heating. These floors are designed to handle the temperature fluctuations that come with radiant heat, ensuring the system works efficiently.
- Carpet: Carpet is not the most efficient option for radiant floor heating because it acts as an insulator, preventing the heat from radiating upward. However, thinner carpets or carpets with low-pile fibers may still work with radiant systems, particularly when combined with a thinner underlayment. While carpets can provide a cozy surface, they might reduce the overall efficiency of your heating system.
Flooring Types to Avoid
While many flooring types are compatible with hydronic radiant heating, others should be avoided due to their poor heat conductivity or their susceptibility to damage from heat exposure. Here are some flooring materials that should be avoided with hydronic radiant floor heating:
- Solid Hardwood: Solid hardwood is sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity, which means it can expand and contract as the temperature fluctuates. Over time, this can cause the floor to warp, crack, or buckle under the constant heat. This type of flooring is not ideal for radiant heating, as the temperature shifts can cause long-term damage.
- Bamboo: Bamboo is often used for its eco-friendly qualities, but it is not recommended for radiant heating systems. Bamboo is a natural material that expands and contracts significantly with changes in temperature. This makes it more susceptible to warping and damage when exposed to the heat generated by hydronic systems.
- Cork: Cork is a soft, insulating material that is commonly used for its comfort and sound-absorbing properties. However, it is a poor conductor of heat and can impede the effectiveness of your radiant heating system. Additionally, cork can become damaged by the constant exposure to heat, which can cause it to lose its structure or integrity over time.
- Rubber Flooring: Rubber flooring is also not suitable for radiant floor heating. Rubber acts as an insulator, which means it blocks heat from passing through to the room. This makes it an inefficient option for radiant heating. Rubber flooring can also degrade when exposed to sustained heat, leading to reduced performance and potential damage.
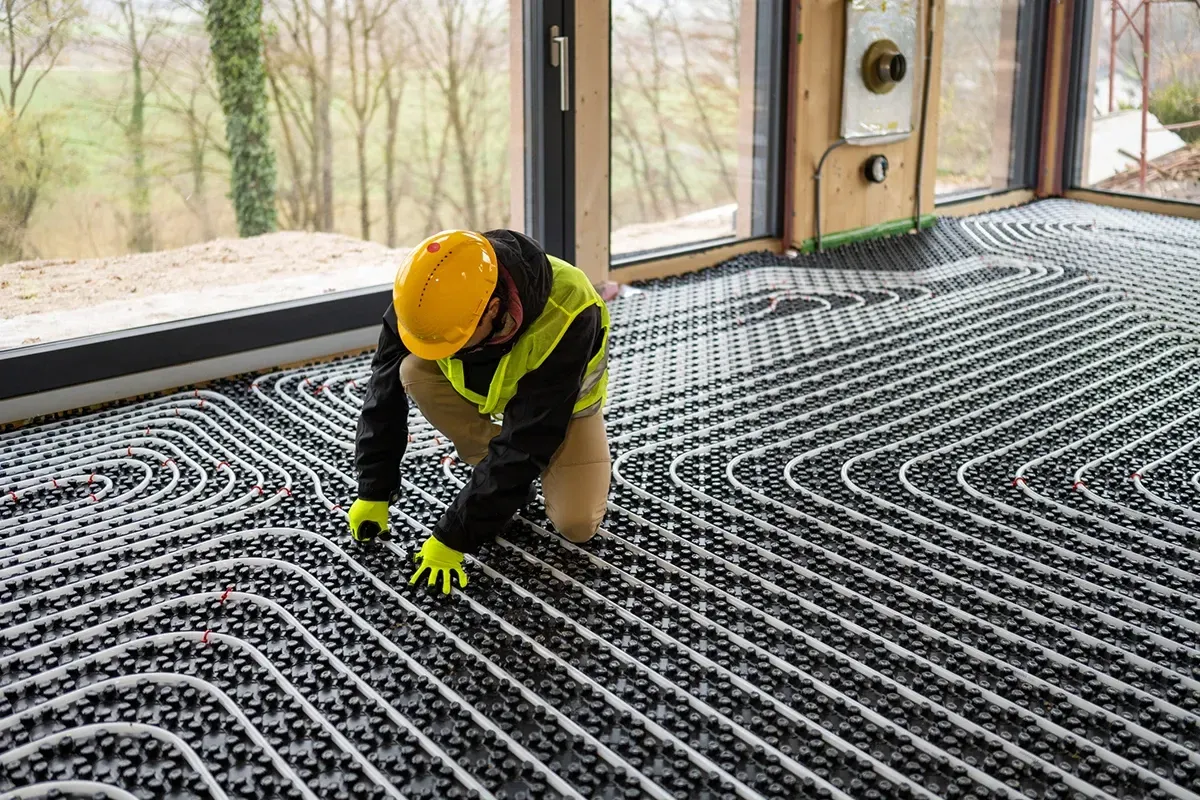
Installation Heated Floors
Proper installation is crucial to the long-term performance of your hydronic radiant heating system. Here are some tips to ensure that your system is installed correctly:
- Insulate Properly: Insulating the subfloor helps prevent heat loss and ensures that the warmth generated by the system is directed upward into the room rather than being absorbed by the ground beneath. Proper insulation helps the system run more efficiently and reduces energy costs.
- Avoid Rapid Temperature Fluctuations: Rapid changes in temperature can damage both your flooring and your hydronic system. It’s important to gradually adjust the temperature of the system to prevent thermal shock, which can cause cracks or other damage to the floor.
- Consult Professionals: Installing a hydronic radiant floor heating system is a complex process that requires specialized knowledge. It is always best to hire a professional who is experienced with radiant heating systems to ensure that your system is installed correctly and operates as efficiently as possible.

Warranty Considerations
One of the most important considerations when installing hydronic radiant floor heating is how it may impact your flooring's warranty. Many flooring manufacturers have strict guidelines about installing radiant heating systems with their products. In some cases, the manufacturer may void the warranty if their flooring is installed with a hydronic heating system, especially if the heat causes the flooring to warp, crack, or expand.
To avoid voiding your warranty, always check with the manufacturer before making a flooring choice. Be sure to verify whether the product is compatible with radiant heating and whether there are any specific installation guidelines that need to be followed. For example, some manufacturers may require the use of specific adhesives or underlayment to ensure compatibility with radiant heat.
FAQ
1. Are heated floors worth it?
Heated floors can be worth the investment if you prioritize comfort, energy efficiency, and even heating. They reduce cold spots and can lower energy bills in well-insulated spaces. However, the upfront installation cost may not suit all budgets, particularly for large areas. They are especially beneficial in bathrooms, kitchens, or regions with cold winters.
2. What is the cost of radiant floor heating?
The cost varies based on the type and size of the system. Electric systems typically cost $8–$15 per square foot for materials and installation, while hydronic systems range from $10–$25 per square foot. Hydronic systems may cost more initially but offer better efficiency for larger areas.
3. What are the disadvantages of radiant floor heating?
- High upfront cost: Installation, especially for hydronic systems, can be expensive.
- Time-consuming installation: Retrofitting radiant heating requires removing existing flooring.
- Inflexibility: Repairs can be challenging since the system is beneath the floor.
- Compatibility concerns: Not all flooring types, like some vinyl or wood, tolerate high heat.
4. Electric vs hydronic radiant floor heating
Electric radiant floor heating is generally easier and less expensive to install, making it ideal for smaller spaces or renovations. It uses electric cables or mats to produce heat but can be costly to operate long-term, especially in larger areas. Hydronic systems, on the other hand, use heated water circulated through tubes beneath the floor. These systems have higher upfront installation costs but are more energy-efficient for heating larger spaces, particularly in colder climates. The choice between the two depends on budget, project size, and energy efficiency priorities.
5 Can you install heated floors under LVP?
Yes, you can install radiant heating under luxury vinyl plank (LVP) flooring, but you must ensure the system's temperature does not exceed the manufacturer’s heat tolerance, typically around 80–85°F, to avoid damaging the vinyl.
6. How to adjust radiant floor heating?
Radiant heating systems often include programmable thermostats to adjust temperatures. Hydronic systems can also be controlled using zone valves or manifolds to heat specific areas. Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance and avoids overheating.
7. Are heated floors dangerous?
Heated floors are generally safe when installed and maintained properly. Electric systems have built-in safety features, such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), to prevent electrical hazards. Hydronic systems use water, reducing the risk of electrical issues, but proper installation is essential to avoid leaks. Overheating is rare but can damage flooring if systems are not set to appropriate temperatures. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and have systems installed by professionals to ensure safety.
Conclusion
Hydronic radiant floor heating offers a host of benefits, including energy efficiency, even heat distribution, and a comfortable, quiet environment. To ensure that your system works efficiently, it’s essential to choose the right flooring material. Tile, stone, and certain engineered hardwood floors are the best options for radiant heat, while materials like solid hardwood, bamboo, cork, and rubber should be avoided due to their poor heat conductivity or vulnerability to damage from heat.
At Rejuvenation Floor and Design, we’re committed to helping you select the perfect flooring and heating solutions for your home. Our team of experts can guide you through the process, ensuring that your radiant floor heating system and flooring are a perfect match.